With Claude
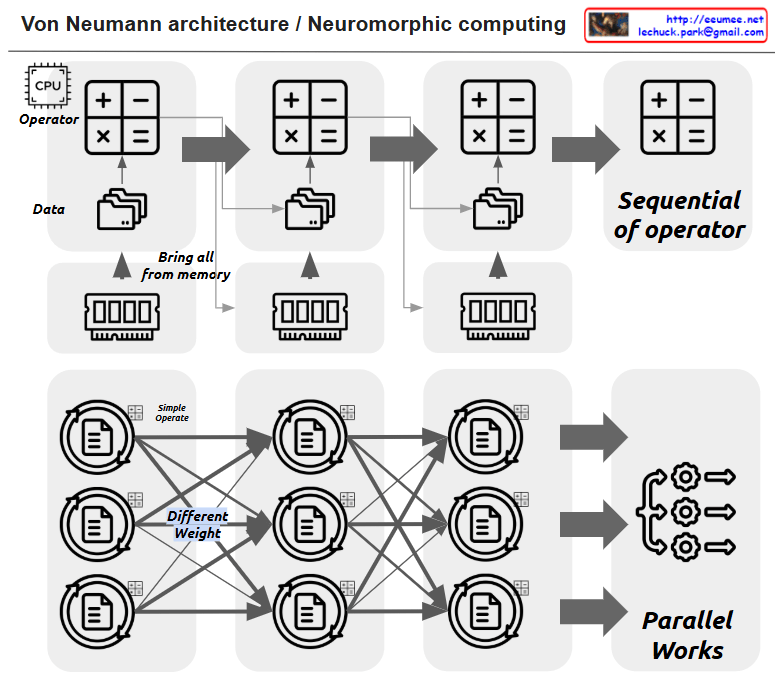
This image illustrates the comparison between Von Neumann architecture and Neuromorphic computing.
The upper section shows the traditional Von Neumann architecture:
- It has a CPU (Operator) that processes basic operations (+, -, ×, =) sequentially
- Data is brought from memory (“Bring all from memory”) and processed in sequence
- All operations are performed sequentially (“Sequential of operator”)
The lower section demonstrates Neuromorphic computing:
- It shows a neural network structure where multiple nodes are interconnected
- Each connection has different weights (“Different Weight”) and performs simple operations (“Simple Operate”)
- All operations are processed in parallel (“Parallel Works”)
Key differences between these architectures:
- Von Neumann architecture: Sequential processing, centralized computation
- Neuromorphic computing: Parallel processing, distributed computation, design inspired by the human brain’s structure
The main advantage of Neuromorphic computing is that it provides a more efficient architecture for artificial intelligence and machine learning tasks by mimicking the biological neural networks found in nature. This parallel processing approach can handle complex computational tasks more efficiently than traditional sequential processing in certain applications.
The image effectively contrasts how data flows and is processed in these two distinct computing paradigms – the linear, sequential nature of Von Neumann versus the parallel, interconnected nature of Neuromorphic computing.