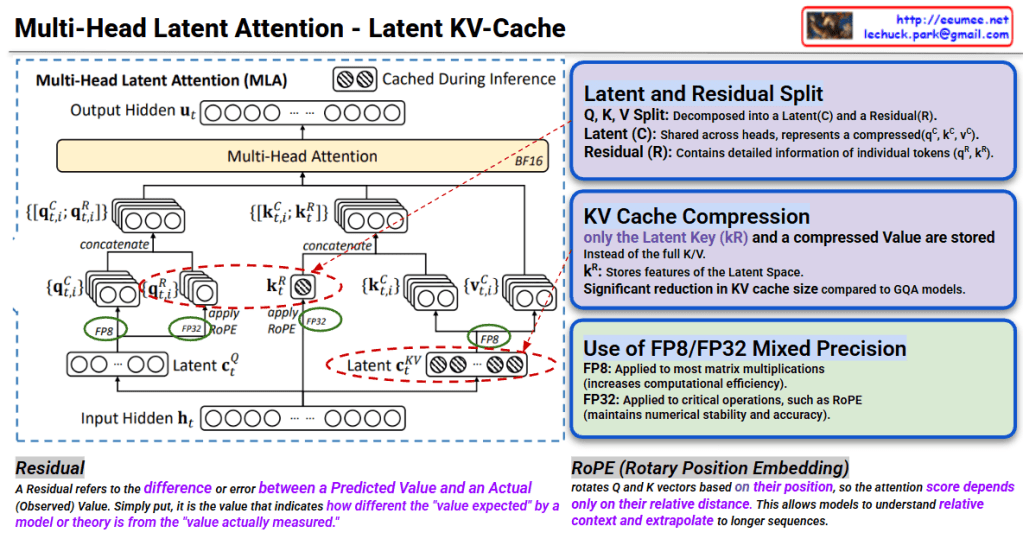
Multi-Head Latent Attention – Latent KV-Cache Interpretation
This image explains the Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA) mechanism and Latent KV-Cache technique for efficient inference in transformer models.
Core Concepts
1. Latent and Residual Split
Q, K, V are decomposed into two components:
- Latent (C): Compressed representation shared across heads (q^c, k^c, v^c)
- Residual (R): Contains detailed information of individual tokens (q^R, k^R)
2. KV Cache Compression
Instead of traditional approach, stores only in compressed form:
- k^R (Latent Key): Stores only Latent Space features
- Achieves significant reduction in KV cache size compared to GQA models
3. Operation Flow
- Generate Latent c_t^Q from Input Hidden h_t (using FP8)
- Create q_{t,i}^C, q_{t,i}^R through Latent
- k^R and v^c are concatenated and fed to Multi-Head Attention
- Caching during inference: Only k^R and compressed Value stored (shown with checkered icon)
- Apply RoPE (Rotary Position Embedding) for position information
4. FP8/FP32 Mixed Precision
- FP8: Applied to most matrix multiplications (increases computational efficiency)
- FP32: Applied to critical operations like RoPE (maintains numerical stability)
Key Advantages
- Memory Efficiency: Caches only compressed representations instead of full K, V
- Computational Efficiency: Fast inference using FP8
- Long Sequence Processing: Enables understanding of long contexts through relative position information
Residual & RoPE Explanation
- Residual: The difference between predicted and actual values (“difference between expected and measured values”)
- RoPE: A technique that rotates Q and K vectors based on position, allowing attention scores to be calculated using only relative distances
Summary
This technique represents a cutting-edge optimization for LLM inference that dramatically reduces memory footprint by storing only compressed latent representations in the KV cache while maintaining model quality. The combination of latent-residual decomposition and mixed precision (FP8/FP32) enables both faster computation and longer context handling. RoPE further enhances the model’s ability to understand relative positions in extended sequences.
#MultiHeadAttention #LatentAttention #KVCache #TransformerOptimization #LLMInference #ModelCompression #MixedPrecision #FP8 #RoPE #EfficientAI #DeepLearning #AttentionMechanism #ModelAcceleration #AIOptimization #NeuralNetworks
With Cluade
