From Claude with some prompting
This image illustrates the flow control and congestion control mechanisms, which are examples of why TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is considered a reliable protocol.
- TCP is a protocol that employs various mechanisms to ensure reliable data transmission.
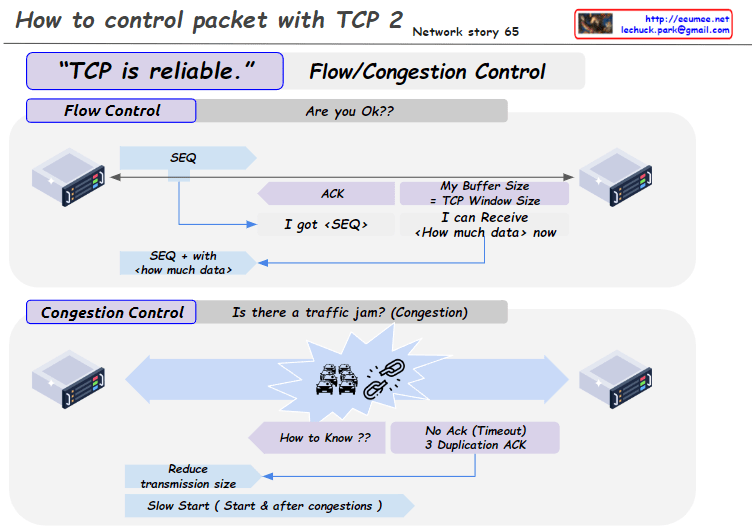
- Flow Control:
- It uses sequence numbers and acknowledgments to regulate the amount of data transmitted based on the receiver’s buffer size, preventing data loss.
- This mechanism contributes to TCP’s reliable delivery guarantee.
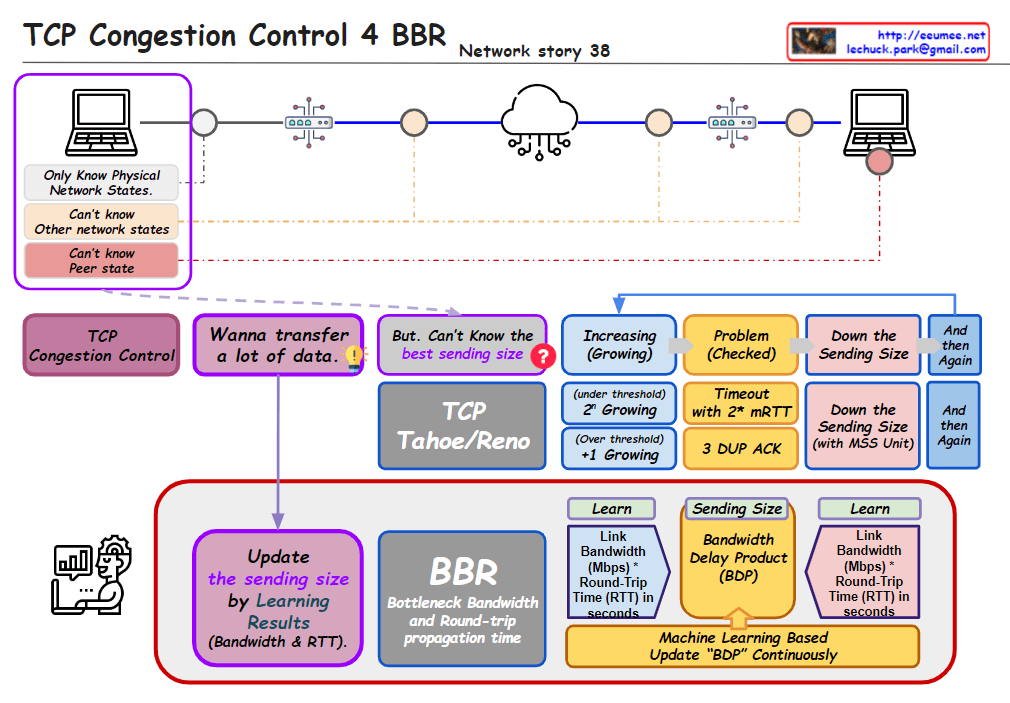
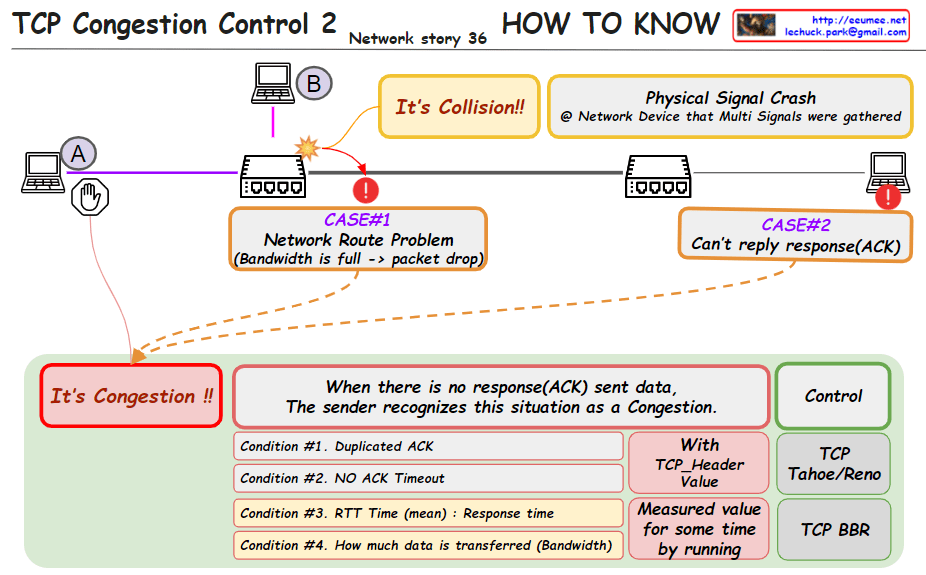
- Congestion Control:
- It detects network congestion and adjusts the transmission rate to avoid further congestion.
- This allows TCP to provide stable and efficient data transfer.
Therefore, flow control and congestion control are key factors that enable TCP to be regarded as a reliable transport protocol. Through these mechanisms, TCP prevents data loss, network overload, and ensures stable communication.