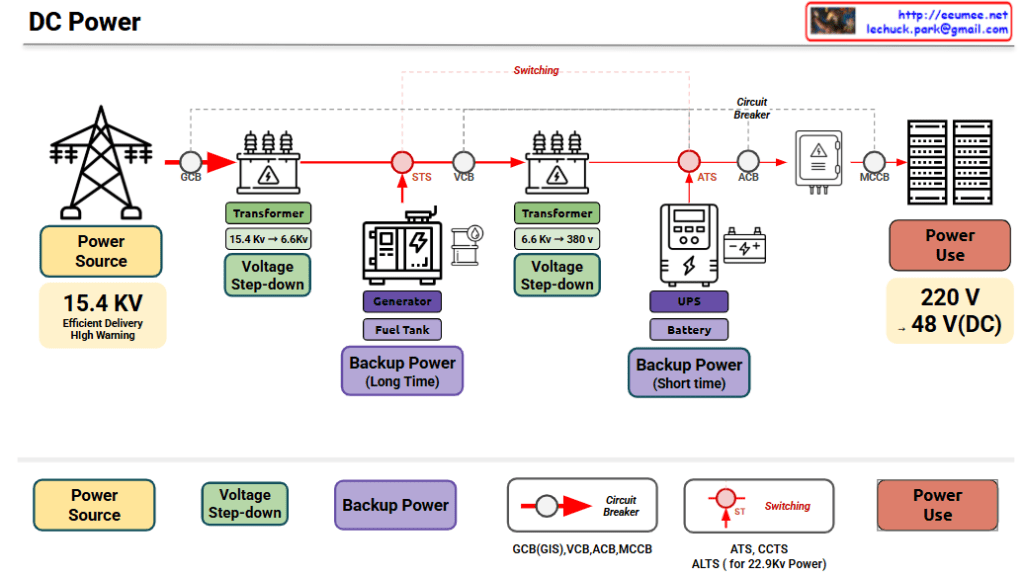
Data Center DC Power System Comprehensive Overview
This diagram illustrates the complete DC (Direct Current) power supply system for a data center infrastructure.
1. Core Components
① Power Source
- 15.4 KV High Voltage AC Power
- Received from utility grid
- Efficient long-distance transmission (Efficient Delivery)
- High voltage warning indicator (High Warning)
② Primary Transformer
- Voltage conversion: 15.4 KV → 6.6 KV
- Function: Steps down high voltage to medium voltage
- Transformation method: Voltage Step-down
- Adjusts voltage for internal data center distribution
③ Backup Power #1 – Generator System (Long-Time Backup)
- Configuration: Diesel generator + Fuel tank
- Characteristic: Long-duration backup capability
- Purpose: Continuous power supply during main power outage
- Advantage: Unlimited operation as long as fuel is supplied
④ Secondary Transformer
- Voltage conversion: 6.6 KV → 380 V
- Function: Steps down medium voltage to low voltage
- Transformation method: Voltage Step-down
- Provides appropriate voltage for UPS and final loads
⑤ Backup Power #2 – UPS System (Short-Time Backup)
- Configuration: UPS + Battery
- Characteristic: Short-duration instantaneous backup
- Purpose: Ensures uninterrupted power during main-to-generator transition
- Role: Supplies power during generator startup time (10-30 seconds)
⑥ Final Load (Power Use)
- Output voltage: 220 V AC or 48 V DC
- Target: Servers, network equipment, storage systems
- Feature: Stable IT infrastructure operation with DC power
2. Voltage Conversion Flow
15.4 KV (AC) → 6.6 KV (AC) → 380 V (AC) → 48 V (DC) / 220 V
[Reception] [Primary TX] [Secondary TX] [Final Conversion]
3. Redundant Backup Architecture
Two-Tier Backup System
Main Power (15.4 KV) ─────┐
├──→ Transform ──→ Load
Generator (Long-term) ────┘
↓
UPS/Battery (Short-term) ──→ Instantaneous uninterrupted guarantee
Backup Strategy:
- Generator: Hours to days operation (fuel-dependent)
- UPS: Minutes to tens of minutes operation (battery capacity-dependent)
- Combined effect: UPS covers generator startup gap to achieve complete uninterrupted power
4. Operating Scenarios
Scenario 1: Normal Operation
Utility power (15.4KV) → Primary transform (6.6KV) → Secondary transform (380V) → UPS → DC load (48V)
Scenario 2: Momentary Power Outage
- Main power interruption detected (< 4ms)
- UPS battery immediately engaged
- Continuous power supply to load with zero interruption
Scenario 3: Extended Power Outage
- Main power interruption detected
- UPS battery immediately engaged (maintains uninterrupted power)
- Generator automatically starts (10-30 seconds required)
- Generator reaches rated capacity and replaces main power
- Generator power charges UPS + supplies load
- Long-term operation with continuous fuel supply
Scenario 4: Generator Failure
- Limited-time operation within UPS battery capacity
- Priority operation for critical systems or graceful shutdown
5. Additional Protection and Control Devices
Supplementary devices for system stability and safety:
Circuit Breaker Hierarchy
- GCB (Generator Circuit Breaker): Primary protection at reception point
- VCB (Vacuum Circuit Breaker): Vacuum interruption, medium voltage protection
- ACB (Air Circuit Breaker): Low voltage distribution panel protection
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker): Individual load protection
- Role: Circuit interruption during overload or short circuit to protect equipment and personnel
Switching Devices
- STS (Static Transfer Switch): High-speed transfer between main power ↔ generator
- ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch): Automatic transfer between power sources ( UPS level)
- ALTS (Automatic Load Transfer Switch): Automatic load transfer ( for 22.9kV class)
- CCTS: Circuit breaker control and transfer system
- Role: Automatic/immediate transfer to backup power during power failure
Switching Points (Red circle indicators)
- Reception point, before/after transformers, backup power injection points
- Critical points for power path changes and redundancy implementation
6. Key System Features
✅ Uninterruptible Power Supply: Three-stage protection with main power → generator → UPS
✅ Multi-stage Voltage Conversion: Ensures both transmission efficiency and usage safety
✅ Automated Backup Transfer: Automatic switching without human intervention
✅ Hierarchical Protection: Stage-by-stage circuit breakers prevent cascading failures
✅ Scalable Architecture: Modular configuration enables easy capacity expansion
Summary
This DC power system architecture ensures continuous, uninterrupted operation of mission-critical data center infrastructure through a sophisticated combination of redundant power sources, automated failover mechanisms, and multi-layered protection systems. The integration of long-term generator backup and short-term UPS battery systems creates a seamless power continuity solution that can handle any grid interruption scenario. The multi-stage voltage transformation (15.4KV → 6.6KV → 380V → 48V DC) optimizes both transmission efficiency and end-user safety while providing flexibility for diverse IT equipment requirements.
#DataCenter #DCPower #PowerSystems #CriticalInfrastructure #UPS #BackupPower #DataCenterDesign #ElectricalEngineering #PowerDistribution #MissionCritical #DataCenterInfrastructure #FacilityManagement #PowerReliability #UninterruptiblePowerSupply #DataCenterOperations
With Claude