Digital Twin System Using CFD and AI/ML
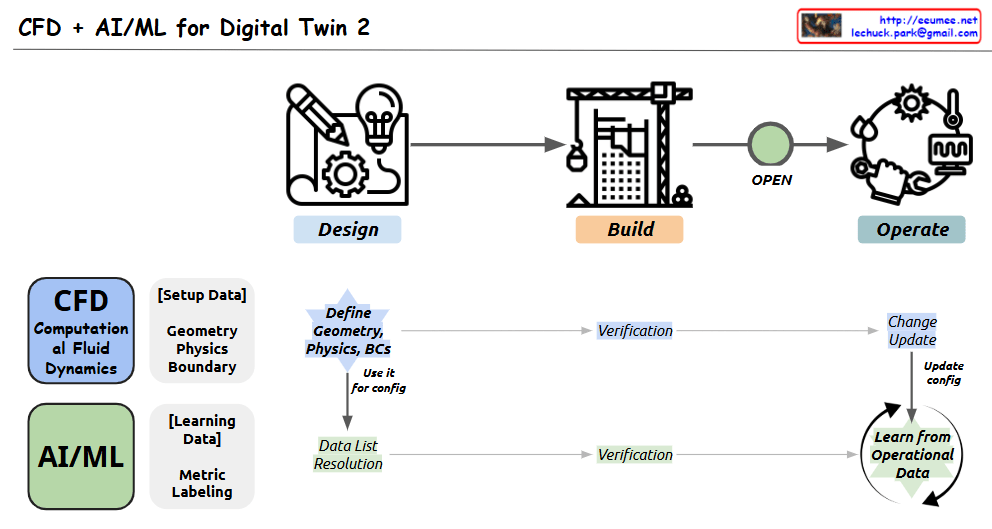
This diagram illustrates the complete lifecycle of a digital twin system, showing how CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) and AI/ML play crucial roles at different stages.
Key Stages
- Design:
- CFD plays a critical role at this stage
- Establishes the foundation through geometric modeling, physical property definition, and boundary condition setup
- Accurate physical simulation at this stage forms the basis for future predictions
- Build:
- Implementation stage for the designed model
- Integration of both CFD models and AI/ML models
- Operate:
- AI/ML plays a critical role at this stage
- System performance prediction and optimization based on real-time data
- Continuous model improvement by learning from operational data
Technology Integration Process
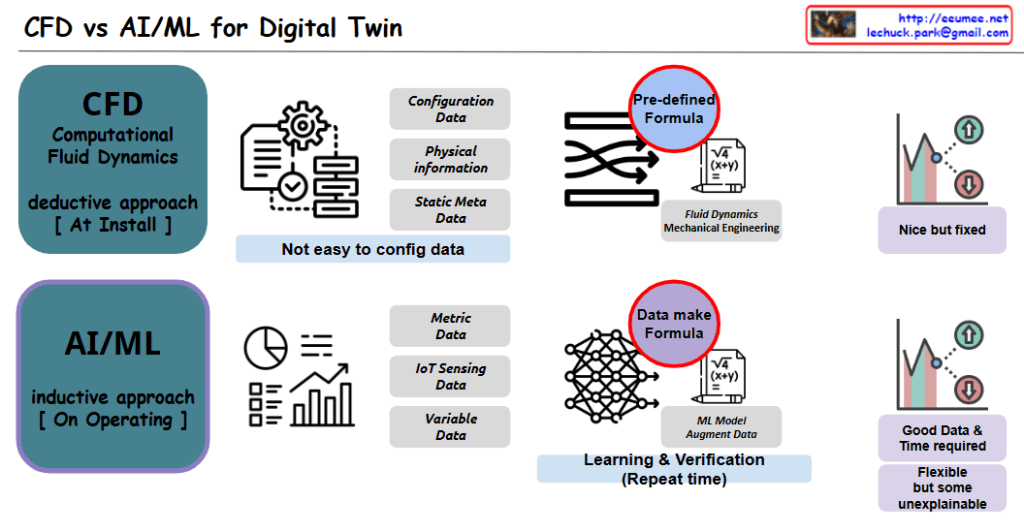
- CFD Track:
- Provides accurate physical modeling during the design phase
- Defines geometry, physics, and boundary conditions to establish the basic structure
- Verifies model accuracy through validation processes
- Updates the model according to changes during operation
- AI/ML Track:
- Configures learning data and defines metrics
- Sets up data lists and resolution
- Provides predictive models using real-time data during the operation phase
- Continuously improves prediction accuracy by learning from operational data
Cyclical Improvement System
The key to this system is that physical modeling (CFD) at the design stage and data-driven prediction (AI/ML) at the operation stage work complementarily to form a continuous improvement cycle. Real data collected during operation is used to update the AI/ML models, which in turn contributes to improving the accuracy of the CFD models.
With Claude