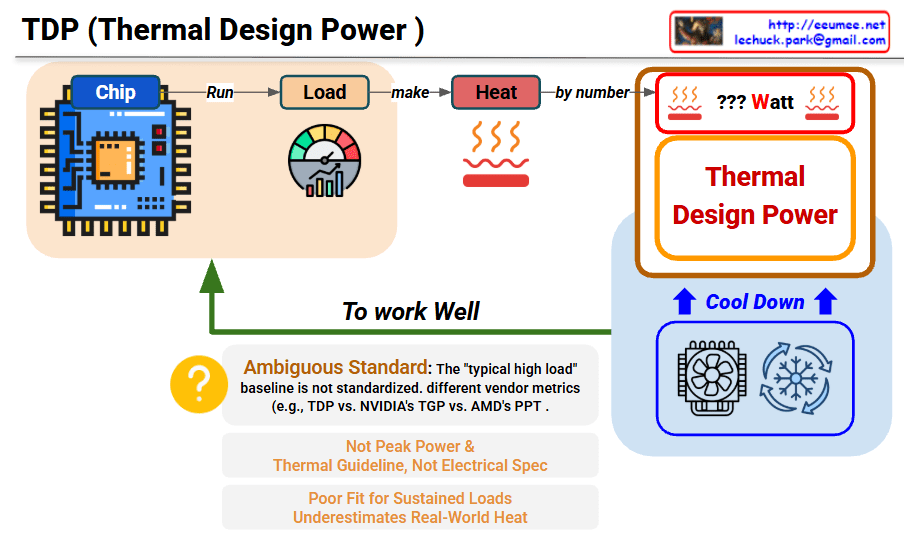
TDP (Thermal Design Power) Interpretation
This image explains the concept and limitations of TDP (Thermal Design Power).
Main Process
Chip → Run Load → Generate Heat → TDP Measurement
- Chip: Processor/chip operates
- Load (Run): Executes specific workload
- Heat (make): Heat is generated (measured by number)
- ??? Watt: Displayed as TDP value
Role of TDP
- Thermal Design Guideline: Reference for cooling system design
- Cool Down: Serves as baseline for cooling solutions like fans and coolers
⚠️ Critical Limitations
Ambiguous Standard
- “Typical high load” baseline is not standardized
- Different measurement methods across vendors:
- Intel’s TDP
- NVIDIA’s TGP (Total Graphics Power)
- AMD’s PPT (Package Power Tracking)
Problems with TDP
- Not Peak Power – Average value, not maximum power consumption
- Thermal Guideline, Not Electrical Spec – Just a guide for thermal management
- Poor Fit for Sustained Loads – Doesn’t properly reflect real high-load scenarios
- Underestimates Real-World Heat – Measured lower than actual heat generation
Summary
TDP is a thermal guideline for cooling system design, not an accurate measure of actual power consumption or heat generation. Different manufacturers use inconsistent standards (TDP/TGP/PPT), making comparisons difficult. It underestimates real-world heat and peak power, serving only as a reference point rather than a precise specification.
#TDP #ThermalDesignPower #CPUCooling #PCHardware #ThermalManagement #ComputerCooling #ProcessorSpecs #HardwareEducation #TechExplained #CoolingSystem #PowerConsumption #PCBuilding #TechSpecs #HeatDissipation #HardwareLimitations
With Claude