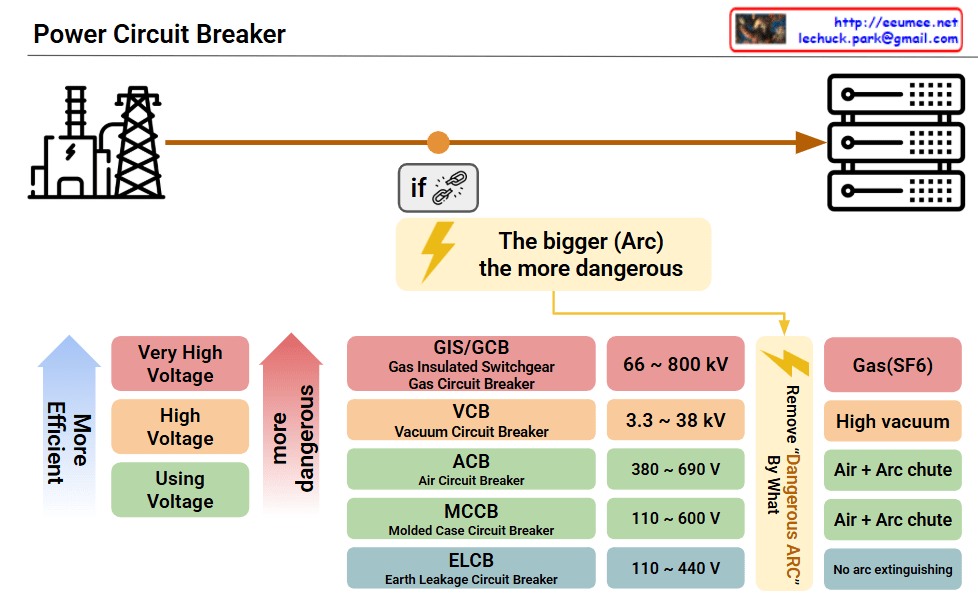
This image presents a Power Circuit Breaker classification diagram showing the types and characteristics of electrical circuit breakers used in power systems.
System Overview
Power Flow: The diagram illustrates the electrical power path from power plant → transmission lines → circuit breakers → distribution panels.
Circuit Breaker Classification
The breakers are categorized by voltage levels and arc extinguishing methods:
Voltage Classifications
- Very High Voltage: 66~800kV
- High Voltage: 3.3~38kV
- Using Voltage: 380~690V, 110~600V, 110~440V
Breaker Types and Arc Extinguishing Methods
- GIS/GCB (Gas Insulated Switchgear/Gas Circuit Breaker)
- 66~800kV
- Uses SF6 gas with high vacuum technology
- VCB (Vacuum Circuit Breaker)
- 3.3~38kV
- Vacuum arc extinguishing method
- ACB (Air Circuit Breaker)
- 380~690V
- Air + arc chute method
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker)
- 110~600V
- Air + arc chute method
- ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
- 110~440V
- Ground fault protection, no arc extinguishing
Key Safety Message
The diagram emphasizes “The bigger (Arc) the more dangerous” – highlighting that higher voltages require more sophisticated and safer arc extinguishing technologies.
Summary: This technical diagram systematically categorizes power circuit breakers from ultra-high voltage (800kV) to low voltage (110V) applications, demonstrating how arc extinguishing complexity increases with voltage levels. The chart serves as an educational reference showing that higher voltage systems require more advanced safety mechanisms like SF6 gas insulation, while lower voltage applications can use simpler air-based arc interruption methods.
With Claude