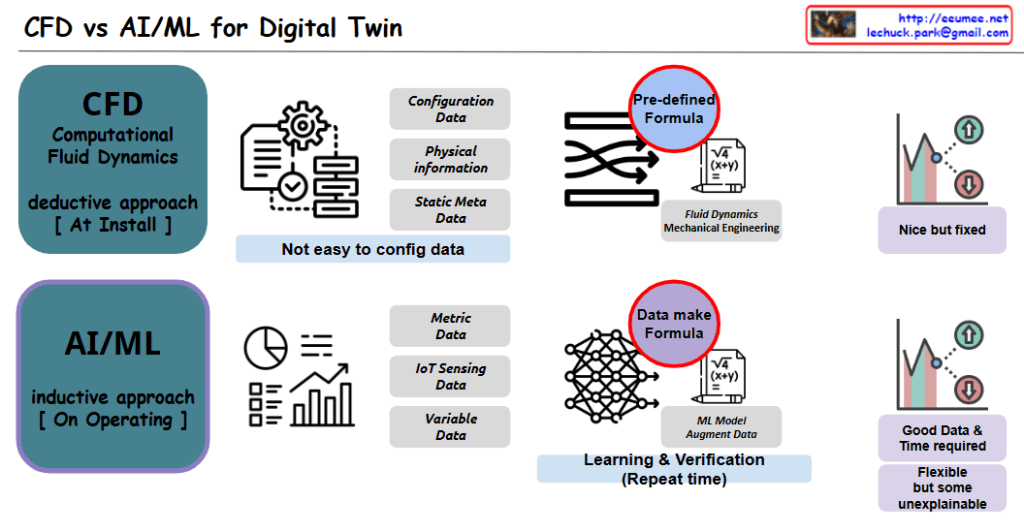
CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) – Deductive Approach [At Installation]
- Data Characteristics
- Configuration Data
- Physical Information
- Static Meta Data
- Features
- Complex data configuration
- Predefined formula usage
- Result: Fixed and limited
- Stable from engineering perspective
AI/ML – Inductive Approach [During Operation]
- Data Characteristics
- Metric Data
- IoT Sensing Data
- Variable Data
- Features
- Data-driven formula generation
- Continuous learning and verification
- Result: Flexible but partially unexplainable
- High real-time adaptability
Comprehensive Comparison
Harmonious integration of both approaches is key to future digital twin technologies
CFD: Precise but rigid modeling
AI/ML: Adaptive but complex modeling
The key insight here is that both CFD and AI/ML approaches have unique strengths. CFD provides a rigorous, physics-based model with predefined formulas, while AI/ML offers dynamic, adaptive learning capabilities. The future of digital twin technology likely lies in finding an optimal balance between these two methodologies, leveraging the precision of CFD with the flexibility of machine learning.
With Claude