From Claude with some prompting
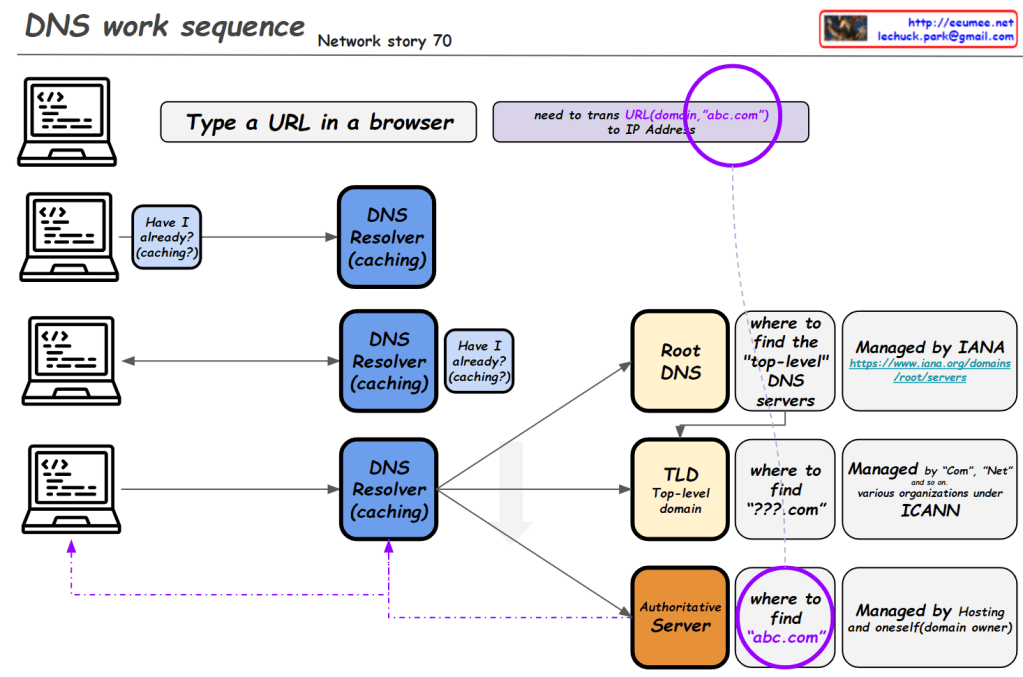
This image illustrates the DNS (Domain Name System) work sequence. Here’s a breakdown:
- It starts with typing a URL in a browser. For example, entering “abc.com” requires translation to an IP address.
- The DNS resolution process begins, involving multiple levels of DNS resolvers with caching capabilities.
- At each level, there’s a “Have I already? (caching?)” check. If the information is cached, it’s used immediately.
- If not found, it proceeds to the next level:
- Root DNS: Provides information on top-level DNS servers (Managed by IANA)
- TLD (Top-Level Domain): Gives information on domains like “.com” (Managed by various organizations under ICANN)
- Authoritative Server: Provides actual domain information (e.g., abc.com, managed by hosting providers or domain owners)
- Through these stages, the system finds the necessary information to ultimately obtain the IP address of the entered domain.
This diagram effectively demonstrates the hierarchical structure of DNS lookup process and the caching mechanism at each stage.
———:)
Ignite your income potential with the explosive Ninja Strategy course! – http://slickwaves.com/
LikeLike