From DALL-E with some prompting
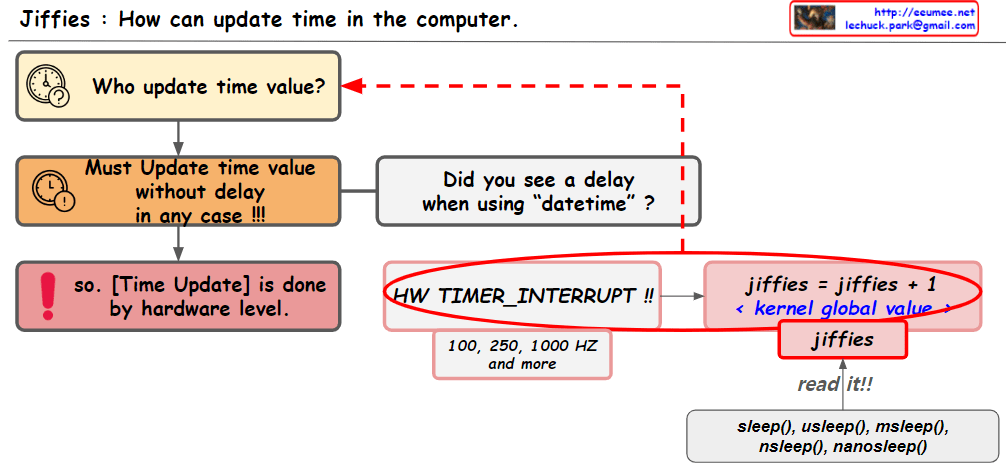
The image provides an explanation of how time updates are handled in computer systems. The key points include:
- “Jiffies” refers to a global variable used by the kernel to keep track of time.
- Time updates are performed at the hardware level through “timer interrupts,” which are initiated periodically by the system’s real-time clock.
- The “HW_TIMER_INTERRUPT” increments the jiffies value by one, and this can be set to various frequencies such as 100, 250, or 1000 Hertz (HZ).
- There is a question about whether there is a delay when using “datetime,” which is crucial as time updates need to be processed in real-time.
- The jiffies value can be read using the
read()function, and functions likesleep(),usleep(),msleep(),nsleep(), andnanosleep()utilize this jiffies value to pause the execution of a program for a certain amount of time.
The image visually represents the concept of how the operating system’s kernel manages time and how time-related functions use the system’s “jiffies” value.