with a claude’s help
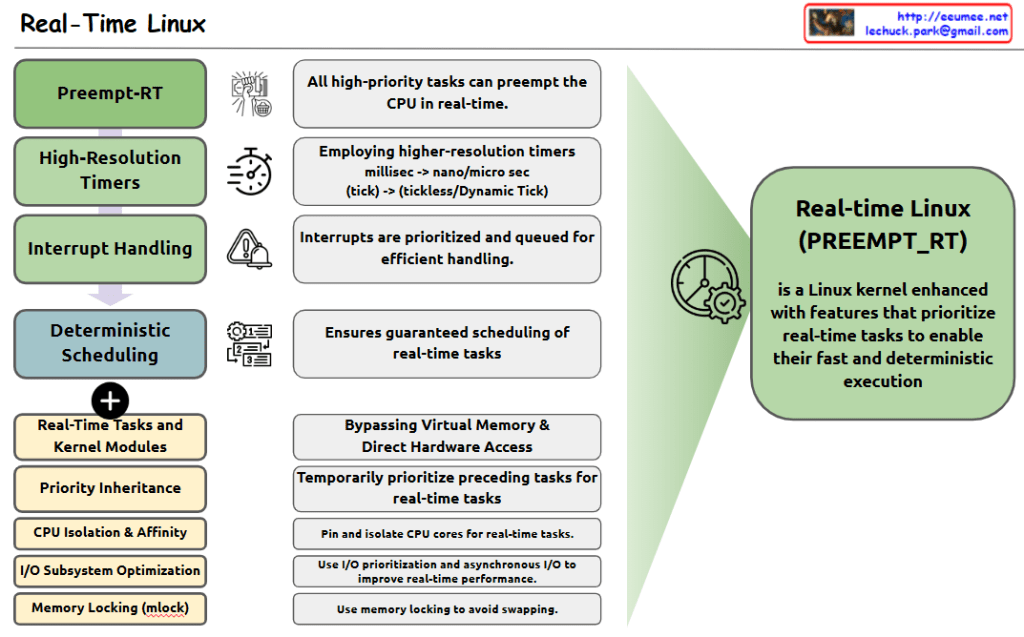
The image shows the key components and features of Real-Time Linux, which is defined as a Linux kernel enhanced with features that prioritize real-time tasks for fast and deterministic execution.
Four Main Components:
- Preempt-RT: All high-priority tasks can preempt the CPU in real-time.
- High-Resolution Timers: Employs higher-resolution timers, shifting from millisec to nano/micro sec (tick -> tickless/Dynamic Tick).
- Interrupt Handling: Interrupts are prioritized and queued for efficient handling.
- Deterministic Scheduling: Ensures guaranteed scheduling of real-time tasks.
Additional Features:
- Real-Time Tasks and Kernel Modules
- Priority Inheritance
- CPU Isolation & Affinity
- I/O Subsystem Optimization
- Memory Locking (mlock)
Key Functionalities:
- Bypassing Virtual Memory & Direct Hardware Access
- Temporarily prioritize preceding tasks for real-time tasks
- Pin and isolate CPU cores for real-time tasks
- Use I/O prioritization and asynchronous I/O to improve real-time performance
- Use memory locking to avoid swapping
The right side of the diagram shows the overall purpose: Real-Time Linux (PREEMPT_RT) is a Linux kernel enhanced with features that prioritize real-time tasks to enable their fast and deterministic execution.
This system is designed to provide predictable and consistent performance for time-critical applications, making it suitable for real-time computing environments where timing precision is crucial.