From Claude with some prompting
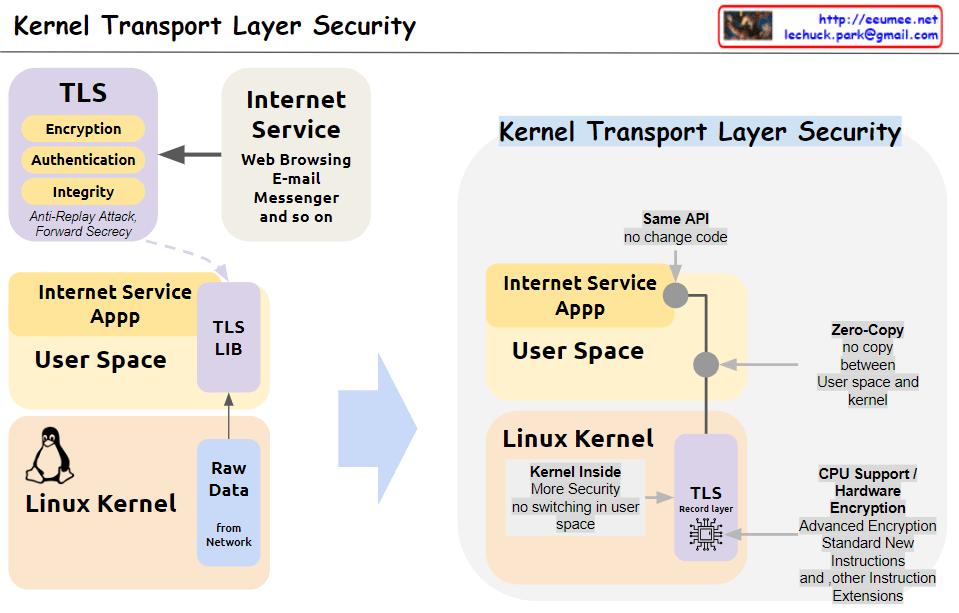
This image illustrates the concept and structure of KTLS (Kernel Transport Layer Security). KTLS implements the TLS protocol within the Linux kernel to improve performance and security.
- The core functionalities of TLS (encryption, authentication, integrity, anti-replay attack, and forward secrecy) are handled within the kernel.
- Applications for internet services (web browsing, email, messenger, etc.) run in user space and utilize the TLS functionality through the TLS library, while still using the same socket API.
- Data copying (Zero-Copy) between user space and kernel space is minimized, enhancing performance.
- With the TLS Record Layer operating inside the kernel, context switching to user space is reduced, improving security.
- Cryptographic acceleration features of CPUs, such as AES-NI and other encryption instruction extensions, are utilized to boost encryption operation performance.
In summary, by moving TLS processing to the kernel level, KTLS significantly improves both performance and security simultaneously.