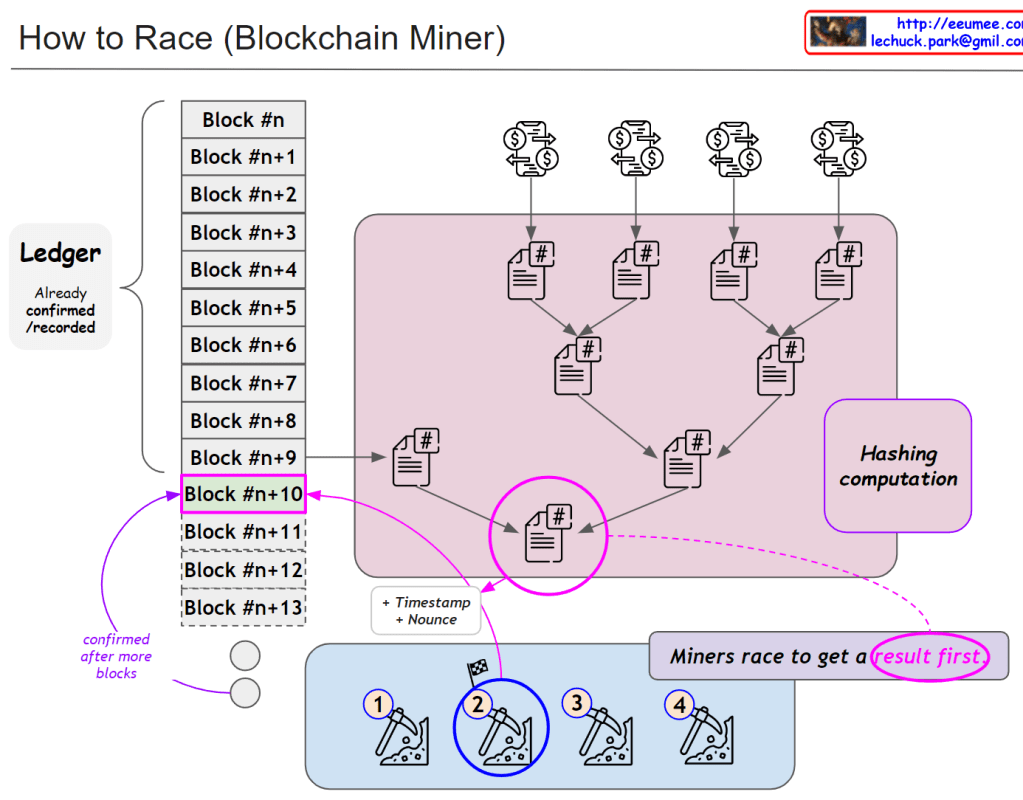
From ChatGPT with some prompting
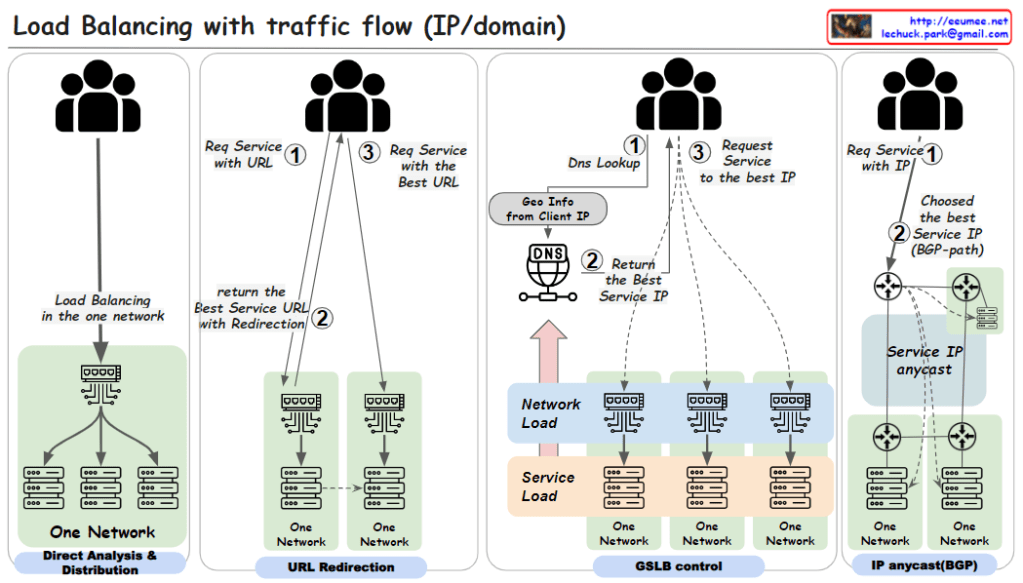
- Direct Analysis & Distribution within One Network:
- This method involves load balancing within a single network using a load balancing switch. The user requests a service via a URL (step 1). The load balancing is handled internally by the switch, which directly analyzes traffic and distributes the load to various servers within the network.
- URL Redirection:
- Here, a user requests a service using a URL (step 1). The network then uses URL redirection to guide the user to the best service URL (step 2), which may involve multiple redirections within one network until the most optimal service endpoint is selected for the user (step 3).
- GSLB (Global Server Load Balancing) Control:
- In this approach, the user starts with a DNS lookup when requesting a service (step 1). The DNS uses the geographic information from the client’s IP to return the best service IP (step 2). The user then requests the service at the given IP address (step 3). This method uses global considerations such as network and service load to balance traffic across multiple networks.
- IP Anycast with BGP (Border Gateway Protocol):
- Users request a service directly using an IP address (step 1). The best service IP is determined via the BGP, which routes traffic based on the shortest available path (step 2). With IP anycast, the user is automatically directed to the nearest or most appropriate service location based on network routing protocols.
Each of these methods is designed to distribute network traffic efficiently. The goal is to ensure service reliability and performance, optimize server use, and improve the overall user experience by reducing latency.