Evolution and Changes: Navigating Through Transformation
Overview:
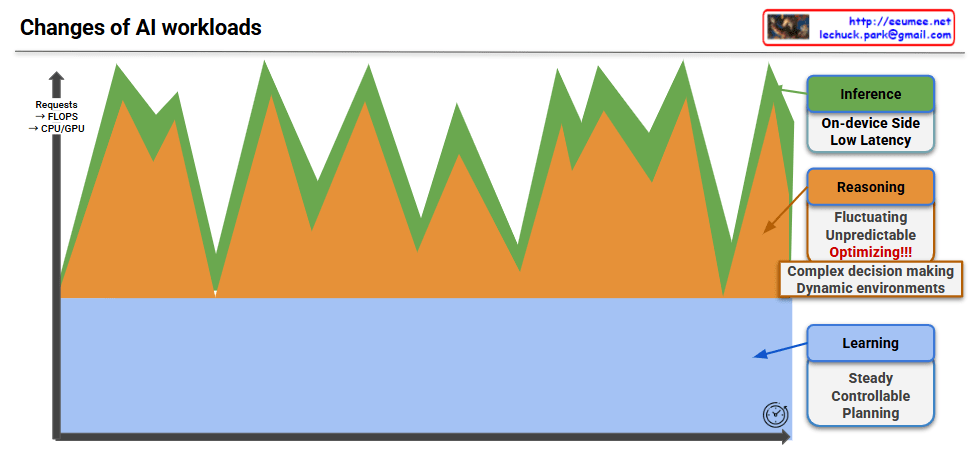
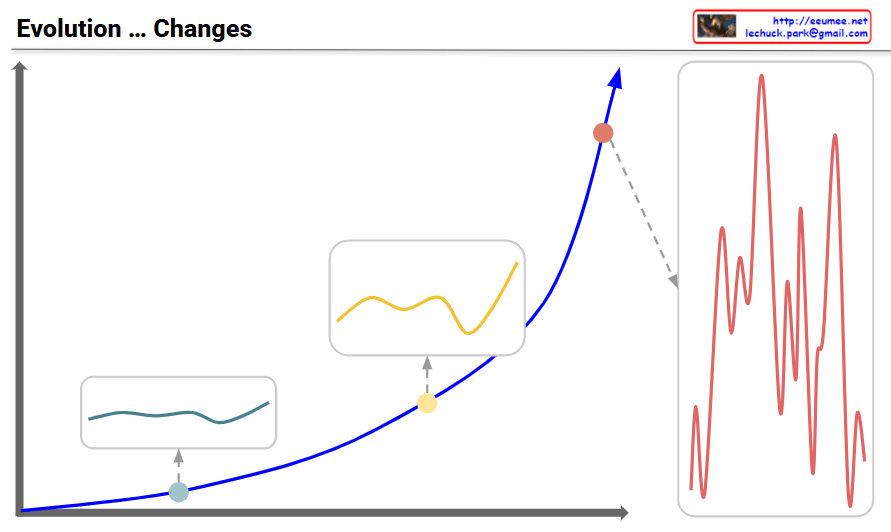
Main Graph (Blue Curve)
- Shows the pattern of evolutionary change transitioning from gradual growth to exponential acceleration over time
- Three key developmental stages are marked with distinct points
Three-Stage Development Process:
Stage 1: Initial Phase (Teal point and box – bottom left)
- Very gradual and stable changes
- Minimal volatility with a flat curve
- Evolutionary changes are slow and predictable
- Response Strategy: Focus on incremental improvements and stable maintenance
Stage 2: Intermediate Phase (Yellow point and box – middle)
- Fluctuations begin to emerge
- Volatility increases but remains limited
- Transitional period showing early signs of change
- Response Strategy: Detect change signals and strengthen preparedness
Stage 3: Turbulent Phase (Red point and box on right – top)
- Critical turning point where exponential growth begins
- Volatility maximizes with highly irregular and large-amplitude changes
- The red graph on the right details the intense and frequent fluctuations during this period
- Characterized by explosive and unpredictable evolutionary changes
- Response Imperative: Rapid and flexible adaptation is essential for survival in the face of high volatility and dramatic shifts
Key Message:
Evolution progresses through stable initial phases → emerging changes in the intermediate period → explosive transformation in the turbulent phase. During the turbulent phase, volatility peaks, making the ability to anticipate and actively respond critical for survival and success. Traditional stable approaches become obsolete; rapid adaptation and innovative transformation become essential.
#Evolution #Change #Transformation #Adaptation #Innovation #DigitalTransformation
With Claude