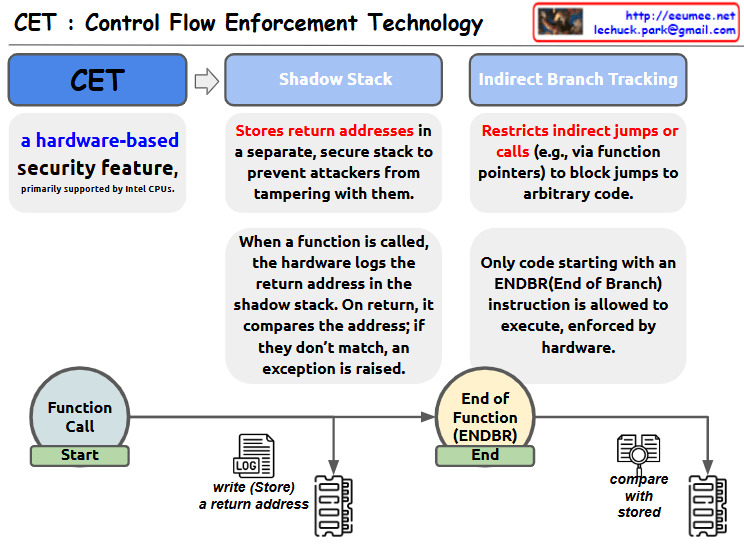
This image is an illustrative diagram of Control Flow Enforcement Technology (CET). CET is a hardware-based security feature, primarily supported by Intel CPUs.
The diagram shows the two main mechanisms of CET:
- Shadow Stack:
- Stores the return address on a separate, secure stack to prevent an attacker from changing it.
- When a function is called, the hardware writes the return address to the shadow stack.
- When the function returns, the address on the stack is compared to the address on the shadow stack, and an exception is thrown if they don’t match.
- Indirect Branch Tracking:
- Restricts indirect jumps or calls via function pointers, etc. to prevent jumps to arbitrary code.
- Hardware enforces that only code that starts with an End of Branch (ENDBR) instruction can be executed.
At the bottom of the diagram is a visual representation of the process of calling a function and exiting the function with the ENDBR instruction. This shows the process of logging (storing) the return address when the function is called and comparing it to the stored address when the function exits.
With Claude