From DALL-E with some prompting
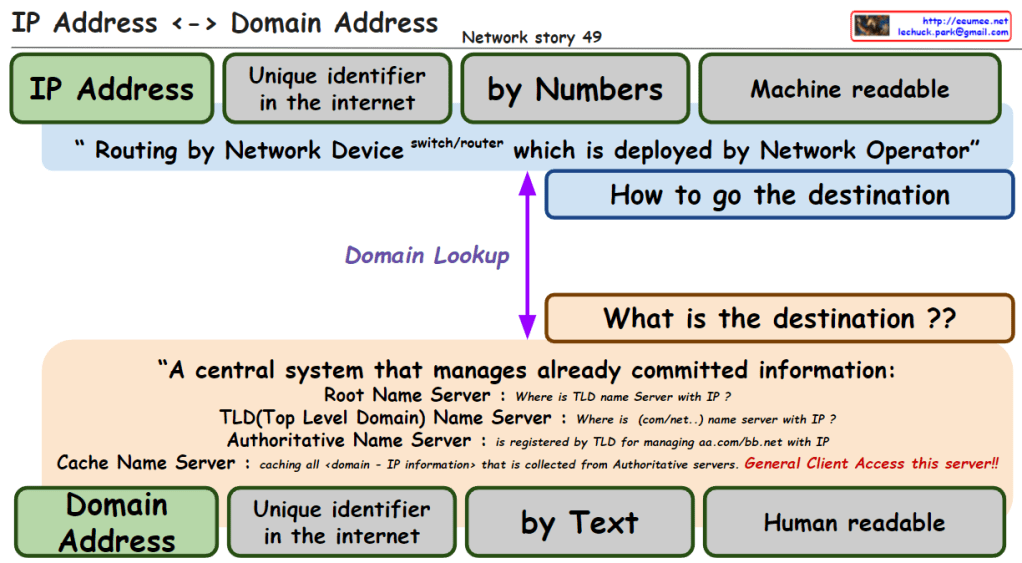
The image explains the relationship between IP addresses and domain addresses within the context of the internet and network infrastructure. Here’s a breakdown of the components:
- IP Address: Identified as a unique identifier in the internet by numbers, which is machine-readable. It is used for routing by network devices like switches and routers, deployed by network operators.
- Domain Lookup: The process that determines how to get the destination, asking “what is the destination?”
- Domain Address: Also a unique identifier on the internet, represented by text, which is human-readable.
- Central System of Name Servers:
- Root Name Server: Answers queries about the location of the Top-Level Domain (TLD) name server associated with an IP.
- TLD Name Server: Provides information about the domain’s name server associated with certain domain extensions like .com or .net.
- Authoritative Name Server: Holds the definitive records for domains within its TLD.
- Cache Name Server: Caches all domain-to-IP information collected from authoritative servers, accessible to general clients.
The overall message emphasizes the conversion between IP addresses (numeric form) and domain addresses (text form), which is crucial for navigating the internet and finding the correct destination for data packets. It also highlights the significance of the Domain Name System (DNS) in translating between human-readable domain names and machine-readable IP addresses.